To begin with,
Let us watch this video that describe about the basic of HTML...
So do you get the idea of what HTML really is???
That was just part of the video. You can continue to watch it here.
HyperText Markup Language (HTML) is the main markup language for displaying web pages and other information that can be displayed in a web browser.
HTML is written in the form of HTML element consisting of tags enclosed in angle brackets (like
<html>), within the web page content. HTML tags most commonly come in pairs like <h1> and </h1>, although some tags, known as empty elements, are unpaired, for example <img>.
The first tag in a pair is the start tag, the second tag is the end tag (they are also called opening tags and closing tags). In between these tags web designers can add text, tags, comments and other types of text-based content.
The purpose of a web browser is to read HTML documents and compose them into visible or audible web pages. The browser does not display the HTML tags, but uses the tags to interpret the content of the page.
HTML elements form the building blocks of all websites. HTML allows images and objects to be embedded and can be used to create interactive forms.
It provides a means to create structured documents by denoting structural semantics for text such as headings, paragraphs, lists, links, quotes and other items.
It can embed scripts in languages such as JavaScript which affect the behavior of HTML webpages.
Markup
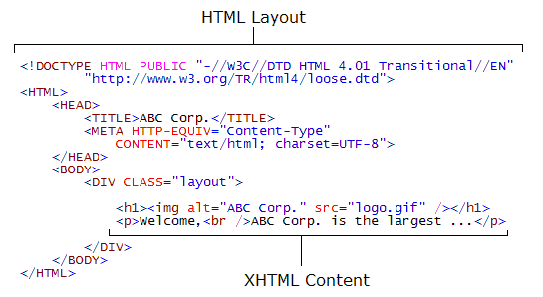
HTML markup consists of several key components, including elements (and their attributes), character-based data types, character references and entity references. Another important component is the document type declaration, which triggers standards mode rendering.
Example
(The text between <html> and </html> describes the web page, and the text between <body> and </body> is the visible page content. The markup text '<title>Hello HTML</title>' defines the browser page title.)
Elements
HTML documents are composed entirely of HTML elements that, in their most general form have three components: a pair of tags, a "start tag" and "end tag"; some attributes within the start tag; and finally, any textual and graphical content between the start and end tags, perhaps including other nested elements.
The HTML element is everything between and including the start and end tags. Each tag is enclosed in angle brackets.
The general form of an HTML element is therefore:
<tag attribute1="value1" attribute2="value2">content</tag>. Some HTML elements are defined as empty elements and take the form <tag attribute1="value1" attribute2="value2" >.
Empty elements may enclose no content. The name of an HTML element is the name used in the tags.
Note that the end tag's name is preceded by a slash character, "/", and that in empty elements the end tag is neither required nor allowed. If attributes are not mentioned, default values are used in each case.
For addition, there are some types of special character and its HTML code:
For addition, there are some types of special character and its HTML code:
| Desired Character | HTML required |
|---|---|
| < | < |
| > | > |
| & | & |
| “ | " |
| non breaking space | |
There are much more knowledge about HTML that cannot be explained here...
For more info..visit here
No comments:
Post a Comment